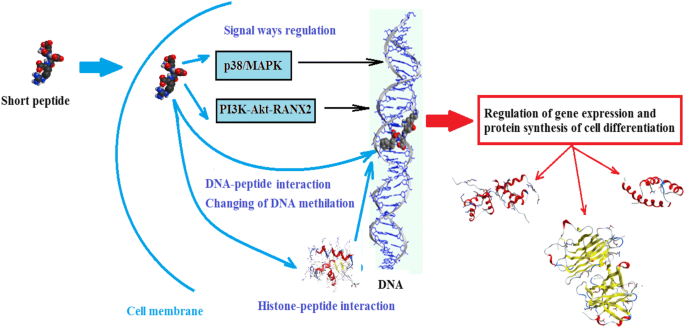
Epitalon, also known as epithalon or epitalone, is a synthetic tetrapeptide consisting of four amino acids – alanine, glutamic acid, aspartic acid, and glycine. It was first isolated from the pineal gland of cows in the 1980s by Russian scientist Vladimir Khavinson. Since then, it has gained significant attention in the field of anti-aging and longevity research due to its potential therapeutic effects. In this blog post, we will explore the mechanisms of action of epitalon, its various therapeutic applications, and its safety profile.
Exploring the Mechanisms of Action of Epitalon
Epitalon is a telomerase activator, which means that it can stimulate the production of telomerase – an enzyme responsible for maintaining the length of telomeres. Telomeres are protective caps at the end of chromosomes that shorten with each cell division and are considered a marker of biological aging. By activating telomerase, epitalon can potentially slow down the shortening of telomeres and delay the onset of age-related decline.
Apart from its role in telomere maintenance, epitalon also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It can scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, thereby protecting cells from damage. Additionally, it can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are molecules involved in the inflammatory response. This dual action of epitalon makes it a promising candidate for various health conditions.
The Role of Epitalon in Cellular Protection and Repair
One of the key mechanisms of epitalon’s action is its ability to protect and repair cells. As mentioned earlier, it has potent antioxidant properties that can neutralize free radicals and prevent cellular damage. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause oxidative stress, leading to DNA damage, cellular dysfunction, and ultimately, aging. By reducing the levels of free radicals, epitalon can help maintain the integrity of cells and tissues.
Moreover, epitalon has been shown to stimulate the production of heat shock proteins (HSPs). These proteins play a crucial role in cellular protection and repair by helping to refold damaged proteins and prevent their aggregation. HSPs are also involved in regulating cell growth and survival, making them essential for maintaining overall cellular health. By increasing the production of HSPs, epitalon can enhance the body’s ability to cope with stressors and promote longevity.
Epitalon’s Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
In addition to its role in cellular protection and repair, epitalon also has potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Oxidative stress and inflammation are two key drivers of aging and age-related diseases. By reducing oxidative stress and inhibiting inflammation, epitalon can potentially slow down the aging process and improve overall health.
A study published in the journal Aging and Disease demonstrated the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of epitalon in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. The researchers found that treatment with epitalon reduced oxidative stress markers and inhibited the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, leading to improved cognitive function and reduced brain damage. This suggests that epitalon may have potential therapeutic applications in neurodegenerative disorders.
Therapeutic Applications of Epitalon: A Critical Review
Epitalon has been studied extensively for its potential therapeutic applications. While most of the research has been conducted on animal models, there is growing evidence to support its use in humans as well. Let’s take a closer look at some of the areas where epitalon has shown promising results.
Epitalon in Aging Research: Delaying the Onset of Age-Related Decline
Aging is a complex process characterized by the gradual decline of physiological functions, leading to an increased risk of age-related diseases. Telomere shortening is considered one of the hallmarks of aging, and epitalon’s ability to activate telomerase has made it a popular subject of research in the field of anti-aging.
A study published in the journal Aging Cell showed that treatment with epitalon led to an increase in telomere length in human cells. This suggests that epitalon may have the potential to delay the onset of age-related decline by preserving telomere length. Another study conducted on elderly patients with hypertension found that treatment with epitalon improved their overall health and quality of life, including better sleep, increased energy levels, and improved cognitive function.
The Role of Epitalon in Neurological Disorders: A Promising Neuroprotective Agent
Neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease are characterized by the progressive loss of neurons and impaired brain function. As mentioned earlier, epitalon has shown promising results in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. But its potential extends beyond just this condition.
A study published in the journal Neuroscience Letters demonstrated that epitalon can protect against neuronal damage caused by oxidative stress. The researchers induced oxidative stress in rat brain cells and found that treatment with epitalon reduced cell death and prevented DNA damage. This suggests that epitalon may have neuroprotective effects and could potentially be used in the treatment of various neurological disorders.
Epitalon’s Effects on Metabolism and Energy Production
Apart from its role in aging and neuroprotection, epitalon has also been studied for its effects on metabolism and energy production. A study published in the journal Experimental Gerontology showed that treatment with epitalon improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in rats with metabolic syndrome. This suggests that epitalon may have potential applications in the management of metabolic disorders such as diabetes.
Moreover, epitalon has been shown to increase the production of ATP – the primary source of energy in cells. This can potentially improve overall energy levels and reduce fatigue. A study conducted on athletes found that treatment with epitalon improved their physical performance and increased their endurance. These findings suggest that epitalon may have potential applications in sports performance and recovery.
Epitalon in Cancer Research: Evaluating Its Anti-Tumor Potential
Cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, and finding effective treatments for this complex disease is a top priority for researchers. While there is limited research on epitalon’s effects on cancer, some studies have shown promising results.
A study published in the journal Oncotarget demonstrated that epitalon can inhibit the growth of breast cancer cells by inducing cell death. The researchers also found that epitalon can sensitize cancer cells to chemotherapy, making it a potential adjuvant therapy for cancer treatment. However, more research is needed to fully understand epitalon’s role in cancer prevention and treatment.
Epitalon’s Safety and Toxicity Profile: Weighing the Risks and Benefits
As with any new drug or supplement, it is essential to consider its safety and toxicity profile before using it. While epitalon has shown promising results in various studies, there is limited information available on its long-term effects in humans.
A study published in the journal Regulatory Peptides evaluated the safety and toxicity of epitalon in rats. The researchers found no adverse effects even at high doses, suggesting that epitalon is relatively safe for use. However, more research is needed to determine its long-term effects and potential interactions with other medications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, epitalon is a novel peptide with significant therapeutic potential. Its ability to activate telomerase, protect and repair cells, and reduce oxidative stress and inflammation make it a promising candidate for various health conditions. While more research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action and long-term effects, epitalon shows great promise in the fields of anti-aging, neuroprotection, metabolism, and cancer research. As with any new treatment, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating epitalon into your regimen.